A patent is your ticket to owning your game-changing inventions—but only if you choose the right guide. Navigating the patent process isn’t simple. However, one common question inventors and businesses face is: Should I work with a patent attorney or a patent agent?
Whether you’re comparing a patent attorney vs patent agent or initiating a patent attorney agent search, the choice you make can significantly impact your patent application’s success, legal protections, and long-term business strategy.
In this blog, we’ll break down the key differences between patent attorneys and patent agents, helping you make an informed decision on which expert best suits your needs.
Understanding Patent Attorneys
- What is a Patent Attorney?
A patent attorney is a licensed legal professional who specializes in intellectual property law—particularly patents. They possess both a law degree and a technical background (typically in science or engineering), enabling them to help inventors secure, defend, and enforce their innovations. - Roles and Responsibilities
Patent attorneys guide clients through the entire patent process. Their duties include:
○ Drafting and filing patent applications
○ Prosecuting applications before the USPTO
○ Advising on patentability and intellectual property strategy
○ Representing clients in legal proceedings for patent disputes and infringement cases
- Legal Representation & Patent Prosecution
Additionally, patent attorneys represent clients in negotiations, litigation, and enforcement actions. Their legal expertise is crucial if you are weighing a patent lawyer vs patent agent scenario where court representation becomes a key factor.
- Education and Certification Requirements
To practice as a patent attorney, one must:
○ Earn a law degree and a technical degree or equivalent technical training
○ Successfully pass the United States patent bar exam
Understanding Patent Agents
- What is a Patent Agent?
A patent agent is a technical professional who is registered with the USPTO to represent inventors in patent matters. They are qualified to prepare, file, and prosecute patent applications - Roles and Responsibilities
Patent agents focus primarily on the technical and procedural aspects of patent work. Their roles include:
○ Patent Preparation and Filing
○ Patent Prosecution Support
○ Handling correspondence with the USPTO
- Education and Certification Requirements
To become a patent agent, candidates typically need:
○ A bachelor’s degree in a recognized technical field (such as engineering, chemistry, or physics).
○ To pass the USPTO registration (patent bar) exam
Key Differences Between Patent Attorneys and Patent Agents
1. Legal Privileges and Representation
- Patent Attorney: As fully licensed legal professionals, they can represent clients in all legal matters related to patents—including court litigation and legal negotiations.
- Patent Agent: While highly qualified to handle patent preparation and prosecution before the USPTO, they cannot represent clients in court or provide broad legal advice.
2. Ability to Represent Clients in Court
- Patent Attorney: Can act on behalf of clients in court, advise on infringement litigation, and negotiate settlements in legal disputes.
- Patent Agent: Their practice is limited to the USPTO; they cannot appear in court or litigate patent disputes.
3. Differences in Legal Advisory Roles
- Patent Attorney: Offer comprehensive legal guidance beyond patents—including licensing agreements, contractual issues, and intellectual property strategy.
- Patent Agent: Focus on the technical and procedural aspects of patent applications, without the capacity to advise on broader legal issues.
4. Scope of Services: Comprehensive vs. Specialized
- Patent Attorney: Provide end-to-end legal services that encompass both the technical patent process and additional legal protection strategies, covering various areas of intellectual property law.
- Patent Agent: Deliver specialized services strictly related to patent drafting, filing, and prosecution support, ensuring technical accuracy in patent documents.
5. Cost Considerations
- Patent Attorney: Typically command higher fees due to their broader legal expertise and ability to represent clients in court.
- Patent Agent: Often offer more cost-effective solutions for straightforward patent filing and prosecution, focusing solely on the technical aspects of patent law.
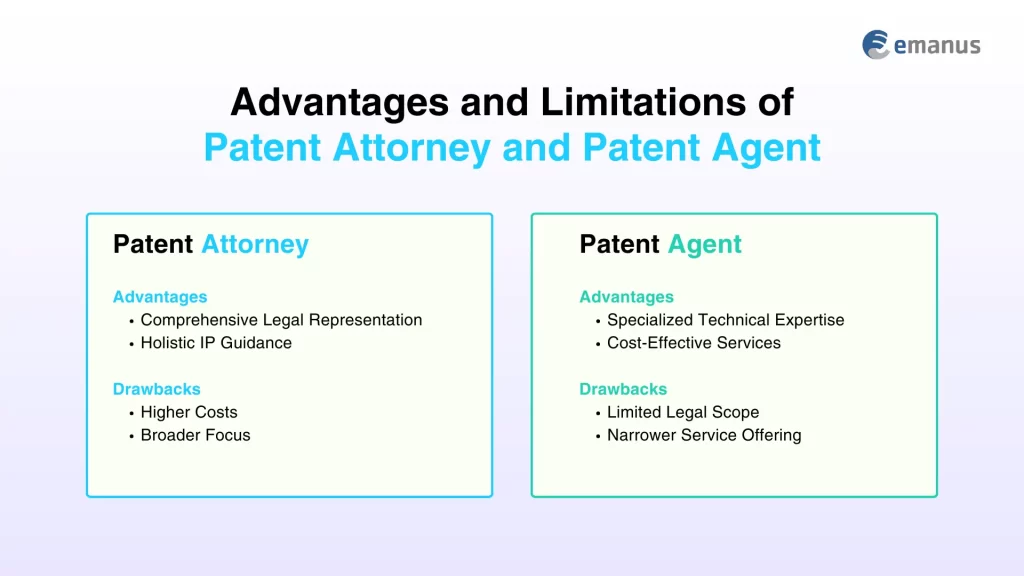
Advantages and Limitations
1. Patent Attorney
Advantages
Comprehensive Legal Representation: They offer full-spectrum legal services including filing patents and court representation.
Holistic IP Guidance: They integrate legal and technical expertise for robust intellectual property protection.
Drawbacks
Higher Costs: Their extensive qualifications generally come with higher fee structures.
Broader Focus: Their wide-ranging services may sometimes overlook specialized technical details.
2. Patent Agent
Advantages
Specialized Technical Expertise: They excel in drafting and prosecuting patent applications with focused technical precision.
Cost-Effective Services: They typically offer more affordable fees for straightforward patent filings.
Drawbacks
Limited Legal Scope: They cannot represent clients in court or provide comprehensive legal advice.
Narrower Service Offering: Their services are confined to patent prosecution without broader IP strategy support.
When to Hire a Patent Attorney vs. a Patent Agent
- Patent Attorney: Ideal for complex inventions, high litigation risk, or when you need comprehensive legal and strategic IP advice.
- Patent Agent: Best suited for straightforward patent filings that require specialized technical drafting at a lower cost.
- Factors to Consider: Assess your invention’s complexity, potential litigation risks, and available budget to determine the right professional.
Before hiring a patent attorney or agent, it’s critical to conduct a thorough patent search to assess your invention’s novelty and avoid infringement issues. Learn how to do it right in our Step-by-Step Guide to Patent Search.
Conclusion
Choosing between a patent attorney and patent agent relies on your invention’s complexity and legal needs. Attorneys offer end-to-end protection—from drafting patents to courtroom defense—while agents excel at cost-effective technical filings.
Still unsure? Don’t risk your IP. Emanus LLC connects you with the right expert to safeguard your invention’s future. Let’s secure your brilliance.
FAQs
What is a patent lawyer?
A patent lawyer is a legal expert who specializes in intellectual property, especially patents. They help inventors secure and protect their inventions through the patent system.
What does a patent attorney do?
A patent attorney prepares, files, and prosecutes patent applications while offering legal advice on protecting inventions. They guide clients through complex legal processes to ensure their ideas are well protected.
What is another name for a patent attorney?
A patent attorney is often simply called a “patent lawyer.” Both terms refer to professionals who specialize in patent law and help safeguard innovative ideas.
Can a patent attorney be an inventor?
Yes, a patent attorney can also be an inventor. However, they need to carefully manage any conflicts of interest to maintain ethical standards while advising clients.






